ZWO ASI678MC/MM 12Bit CMOS Colour Camera
















ZWO ASI678MC/MM 12Bit CMOS Colour Camera
Model - MM | ASI678MM
Why Purchase from All-Star Telescope?
Free Expert Support
Whether you are a first timer needing help with setting up or an enthusiast that can't quite make that one thing work, our expert staff are ready to support your needs. With decades of knowledge and first hand experience we've been there and we can help you through it!
Stress Free, Secure Transactions
You can trust purchasing and delivery with All-Star Telescope. All of our transactions are 100% secure and Level 1 PCI DSS compliant thanks to Shopify's ShopPay platform. For additional protection, we insure 100% of the value of every shipment we make. If it get's lost during shipment, we replace it. If it gets damaged during shipment, we replace it. We make sure your product arrives exactly as you would expect it to; we promise.
We also ensure privacy protection. We never keep any of your credit card information on file and any of your personal data is stored according to our policies.
30 Day Return Policy
Buy with confidence knowing that we accept returns up to 30 days after purchase. We want you to have something you will actually use and we are confident that we keep good quality products in our store with No Junk.
Price Match Promise
Shipping around for the best price is tough, we make it easier by offering the best pricing in the market. But if you find a better price on an in-store item somewhere else we will match it!
Product Description
ASI678MC/MM adopts Sony's latest generation sensor IMX678 with excellent near infrared response. With the advantages of large full well capacity, high dynamic range and low readout noise, this camera has been tested and found to have perfect performance in planetary imaging, solar and lunar imaging.
ASI678MC/MM Features
Clear in Low Light
Thanks to the back-illuminated sensor structure and advanced pixel technology, the camera has very low readout noise and has an ultra-high sensitivity. Especially in low light conditions, the camera performs very well and is able to capture very clear images of celestial objects.
STARVIS 2
ASI678MC/MM can be regarded as an upgrade of ASI178MC. It adopts the latest SONY IMX678 sensor with advanced STARVIS 2 technology. Compared to ASI178MC, this camera features zero amp glow, lower readout noise and higher sensitivity. The dark current noise is greatly decreased; the performance of near infrared is greatly improved.
USB3.0 & 256MB Memory
The camera is equipped with a USB 3.0 transmission interface and a built-in 256MB DDR3 cache to ensure stable and secure data transmission. Under long exposure, it effectively avoids frame dropping and greatly reduces the glow effect caused by slow reading speed.
No Amp Glow
ASI678MC/MM exhibits zero amp glow, no matter how long the exposure and how high the gain value. Since it is implemented directly at the hardware level, it does not require software control.

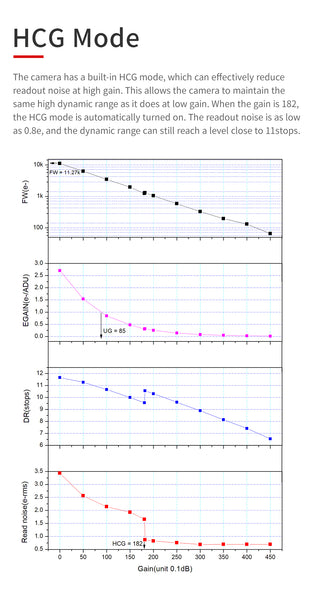
HCG Mode
The camera has a built-in HCG mode, which can effectively reduce readout noise at high gain. This allows the camera to maintain the same high dynamic range as it does at low gain. When the gain is 182, the HCG mode is automatically turned on. The readout noise is as low as 0.8e, and the dynamic range can still reach a level close to 12bit.

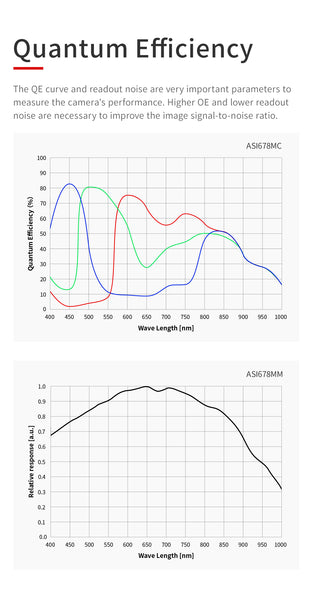
Quantum Efficiency
The QE curve and readout noise are very important parameters to measure the camera's performance. Higher QE and lower readout noise are nec- essary to improve the image signal-to-noise ratio.

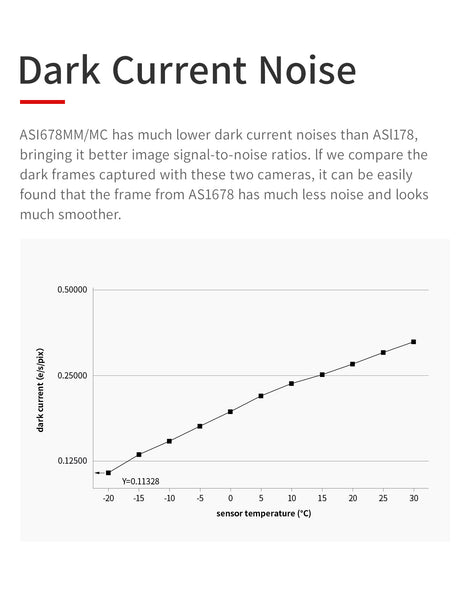
Dark Current Noise
ASI678MC/MM has much lower dark current noises than ASI178, bringing it has better image signal-to-noise ratios. If we compare the darks frames captured with these two cameras, it can be easily found that the frame from ASI678 has much less noise and looks much smoother.

Upgraded from the ASI178MC
The ASI678MC/MM is an upgraded product of the ASI178MC. Compared to the ASI178MC, the ASI678MC/MM has lower read noise, lower dark noise, and no amp glow.
| Model | ASI678MC/MM | ASI178MC |
| Color or Mono | Color | Color |
| With or Without glow | Without | With |
| Format | 1/1.8" | 1/1.8" |
| Resolution | 3840*2160 | 3096*2080 |
| Pixel Size | 2.0μm | 2.4μm |
| Readout Noise | 0.6-2.7e (1e@8db gain) | 1.4-2.2e |
| QE Peak | 83% | 80% |
| Full Well | 11.27ke | 15.0ke |
| ADC | 12bit | 14bit |
| Back Focus | 12.5mm | 12.5mm |
| MAX FPS | 47.5fps | 60fps |
| Diagonal | 8.86mm | 8.95mm |
What's in the Box
Specifications
| Sensor | 1/1.8" CMOS Sony-IMX678AAQR1-C |
| Bayer Pattern | RGGB |
| QE peak | 83% |
| Back focus length | 12.5mm |
| Max fps | 47.5fps |
| Full well | 11.27Ke |
| Shutter | Rolling shutter |
| Resolution | 8.29Mega Pixel, 3840*2160 |
| Pixel Size | 2.0µm |
| Exposure Range | 32μs~2000s |
| Interface | USB 3.0 / USB 2.0 Type-B |
| Protect window | φ21-1.1 AR |
| ADC | 12bit |
| Dimension | 7.68mm*4.32mm |
| Weight | 126g |
| Working Temperature | -5°C~50°C |
| Storage Temperature | -10°C~60°C |
| Working Relative Humidity | 0-80% |
| Supported OS | WIN7/8/10 32&64, Linux, Mac |
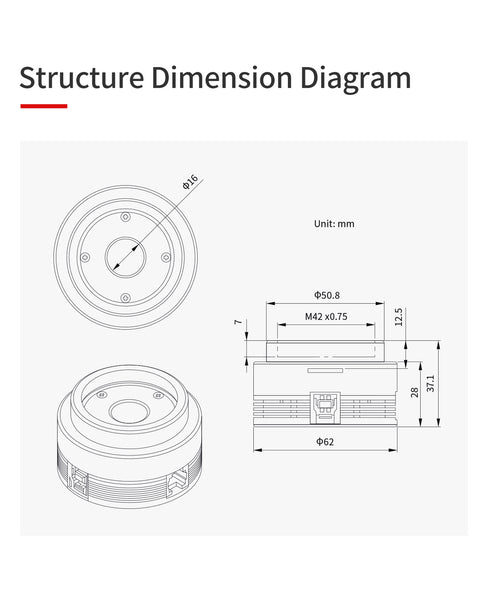
Dimensions

Connection Methods

Additional Articles, Videos, and Links
External Links

Go Ahead, Look at the Sun (With the Right Equipment)
Solar observation and solar photography are a lot of fun with the right equipment, and this is a great time to start. Every 11 years the Sun’s magnetic field completely flips. That means that the...

Astrophotography for Beginners Step 4: Shooting Deep-Sky Images
Taking deep sky pictures can be daunting, luckily there is an easy process to follow to allow you to get great shots! Here is the typical process for actually taking deep-sky images in the field.

Astrophotography for Beginners Step 3: Choosing Gear for Deep-Sky Imaging
Using a star tracker gains you experience with the fundamentals of deep-sky imaging. Shooting the Moon gains you experience focusing and framing through your telescope. Through your sessions you’ll...

Astrophotography for Beginners - Start Here: Getting into Astrophotography Step by Step
Shooting the night sky has never been more popular, nor easier. The choice of equipment has also never been better, or more affordable. However, as per the advice given by Dickinson and Dyer in the...

Astrophotography for Beginners Step 1: Using the Star Adventurer Tracker
By far the most economical and easiest way to capture beautiful images of the Milky Way and large deep-sky objects like the Andromeda Galaxy (shown here) is to use a star tracker. Here are steps an...

Astrophotography for Beginners Step 2: How to Shoot the Moon
Close-ups of the Moon are rewarding, and an easy way to learn to shoot through your telescope. While good results are possible with a phone camera clamped to an eyepiece (as shown below), this tuto...